 Next Generation Networks can be viewed as a ― communication network that allows unfettered access to all communication products and services, irrespective of the service provider or network connection. Basically the boom in the services of wired as well as wireless technologies, both in narrowband as well as broadband environments has created the demand for seamless connectivity between the networks as well as services. This has given rise to a need for an unwired network to support voice, data and video (triple play) over a common network, which is typically called Next Generation Network. In an Next Generation Network environment, it is expected that the consumers will be able to access their voice, data, video and new emerging media applications over a single network.At the same time, the provided service functions are independent from the basic transmission media. All the services are based on the Internet Protocol (IP). The advantage of IP networks is their flexibility and the simple integration of new applications.
Next Generation Networks can be viewed as a ― communication network that allows unfettered access to all communication products and services, irrespective of the service provider or network connection. Basically the boom in the services of wired as well as wireless technologies, both in narrowband as well as broadband environments has created the demand for seamless connectivity between the networks as well as services. This has given rise to a need for an unwired network to support voice, data and video (triple play) over a common network, which is typically called Next Generation Network. In an Next Generation Network environment, it is expected that the consumers will be able to access their voice, data, video and new emerging media applications over a single network.At the same time, the provided service functions are independent from the basic transmission media. All the services are based on the Internet Protocol (IP). The advantage of IP networks is their flexibility and the simple integration of new applications.Pakistan Telecom Authority has established an industry working group with all the major operators and stakeholders to help guide the industry momentum to an effective migration and to resolve any problems that may be faced during transition.
- Hardware standardization.
- Carrier Interconnects in Pakistan, Present and future roadmaps.
- Requirements and framework of end-to-end QoS in NGN.
- Security considerations for NGN networks.
NGN ARCHITECTURE
An idea of a ’Pakistan internet-backbone’ on Gigabit Ethernet (GigE) interface (IP-MPLS) has been proposed which will converge the multi-protocols on an optical backhaul platform i.e. virtually any type of traffic coming from customers networks or other access networks will be converged to one protocol. That is, one protocol from access to core, simplified management throughout the network with flexible service creation and hence Fast Services Roll-out.
(In Pakistan NGN deployments started in 2005 but appreciable activity has been noticed during 2008 & 2009.)
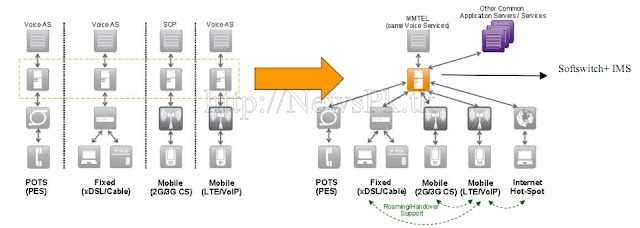
The NGN Networks are categorized into two, The Core Networks and The Access Networks.
The core network of the NGN is an IP network. This is a standardized transport platform consisting of various IP routers and switches. The connection control of the individual components is carried out by the control level. Standard and value-added services can then be provided via the service management level.
All the main stream operators have started their activity in migrating the core networks from legacy to NGN. The incumbent PTCL, having the largest fixed line network has 10 % of its network operating on C5 NGN architecture. The CMTOs, Ufone, Telenor and Mobilink have 100%,75% and 70%of their networks migrated to R4 architecture respectively, with an approved plan for 100% by December 2011.
(PTCL has 10 % of its network operating on C5 NGN architecture. The CMTOs, Ufone, Telenor and Mobilink have 100%,75% and 70%of their networks migrated to R4 architecture respectively.)
- PTCL 5500 Km
- Wateen 5500 Km
- Multinet 4500 Km
- Link Direct 5000 Km
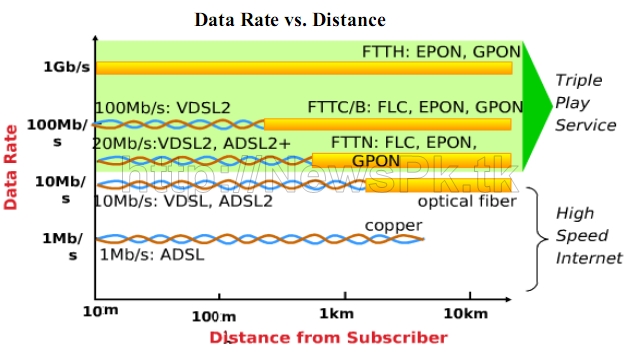
NGN access networks deployment typically refer to network segment which connects an end-user to the nearest location which houses the network access providers’ equipment. So as per the definition , NGN access can be delivered by the network of different technologies including fiber, copper, coaxial as well as different wireless options.
FTTH will make possible NGN’s full capability use. As far as Fiber to the customer premises is concerned it is deemed that it should be able to meet customer requirements, as fiber can offer much more than copper is delivering at the subscriber premises. As far as its affordability is concerned, it will be, undoubtedly, an expensive solution as compared to the existing networks. The OSP(Outside Plant) part of laying fiber is very expensive due to very high ROW charges. Moreover FTTH terminals are also expensive at the moment. This concern of RoI on FTTH is prevailing worldwide and it is a hurdle for the deployment of fiber in access networks specially in the low income regions of the world. The industry members of the NGN-WG came up with special request to the authority to look into the issue of ROW.
(This concern of RoI on FTTH is prevailing worldwide and it is a hurdle for the deployment of fiber in access network.)
- PTCL 12000 Km
- Nayatel 2300 Km
- NTC 637 Km
- World Call 558 Km
a.) Cost Saving:
One of the major drivers of NGN migration is the cost saving, but it is very clear that the NGN-core saves the cost but the deployment of NGN-
access needs a lot of investment to be pooled in. According to an operator “NGN still needs to prove their ROI’s and the total cost of ownership needs to be considered while evaluating such investments.” The market research company Ovum has pointed out that it will take some time before the cost-reduction potential in NGN will becomes noticeable due to more efficient network management. The procedure will take several years.
(It will take some time before the cost-reduction potential in NGN will becomes noticeable due to more efficient network management.)
The other core driver is that, the legacy TDM network equipment is reaching obsolesces and not fully covered by vendor’s support and maintenance contracts.
- Implementation Challenges During Migration (Details Here)
- Dismantled Legacy Assets (Details)
- Bandwidth (Details)
- Convergence across services and markets (Details)
- Tariff/Charging Principles in NGN (Details)
- Commercial Issues in NGN (Details)
- Technical Issues (Details)
- IP-Interconnect Issues (Details)
- Payment for interconnection (Details)
- The location of interconnection points (POI) (Details)
- QoS issues (Details)
- Signaling (Details)
- IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM (IMS) (Details)
(PDF FILE - Size 48 Kilo Bytes)
PTA Website [http://www.pta.gov.pk/media/ngn_report_260111.pdf]
- Cellular Operators Reject 3G in Pakistan
- SMS: Main Source of Mobile Operators Revenue
- With more than a 100 Million Mobile Users - PTA is Changing Lifestyles
- PTA organized seminar on 3G, in collaboration with ZTE (Zhongxing Telecom)







0 comments
Post a Comment