Assignment No. 02
Semester: Spring 2012
CS507-Information Systems
Total Marks: 10
Due Date: 02/5/2012
Assignment
Question 1: (5 Marks)
Consider a garment manufacturing company is newly launched and wants to introduce IT infrastructure in the
organization. Suggest what IT infrastructure will be required for the company to fulfill its requirements.
Solution:-
Building a ‘world-class’ infrastructure ALWAYS starts with the organization structure. Below are recommended organization structures designed for small, medium, and large infrastructure development and support organizations. No one structure is correct; however, it is crucial that key functions be structured to address the people and process issues. These structures are designed to address the people and process issues first with technology being secondary. I’m not saying technology isn’t important but let’s be blunt here based on the 100 plus assessments I’ve performed this data copied from vu solutions dot com infrastructures are in horrible shape because of the lack of attention to these non-technology related issues. For Infrastructure organizations to become successful and cost effective service providers the focus needs to be Organization, People, Process, and Technology in that order.
As I designed these organization structures I included first-, second-, and third-level support roles for each of the areas. I highlight this in the organization charts below because it’s one of the most critical functions that was abandoned as IT organizations transitioned to client/server. It happens to be one of the biggest reasons RAS doesn’t exist in 95% of the IT shops I have visited Organization structure #1 below is designed for IT infrastructure development and support organizations with fewer than 50 employees. The reasons I designed the structure in this manner are:
> Production Control is at the enterprise level for process design, ownership, and accountability. In every small (.com or emerging e-commerce) company I visited priority is always technology, technology, technology. I included a Production Control function to this data copied from vu solutions dot com focus on processes and production QA. Although this is a small shop it’s never to early to start focusing on processes. I’m not trying to change that priority after all it’s what IT is all about-providing Information Technology. We’re asking you to think about process. Once the technology is implemented without the processes high availability for that technology is unrealistic.
> Mission critical (Data Center) functions are separated from non-mission critical functions (Desktop, Help
Desk).
> Level 1, 2, and 3, technical staff for the mission critical production environment is grouped under the same organization to effectively breed future technical resources. All IT organizations have a shortage of technical resources but more so in smaller IT shops.
Organization Structure #1 (for smaller IT organizations)
Organization structure # 2 below is designed for IT departments with 50 to 75 employees. The significance of
this structure is:
> The Production Control function is structured at the enterprise level bringing visibility and accountability
for key this data copied from vu solutions dot com infrastructure process design, ownership, and accountability.
> Service Center (Help Desk) is structured at the enterprise level.
> All mission-critical technical related services are grouped under the Technical Services organizaion.
Organization Structure #2 (for mid-size IT organizations)
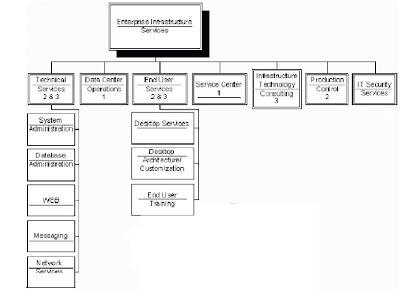
Organization structure # 3 below is designed for larger IT departments with 75+ employees. The significance of this structure is:
To introduce an Infrastructure Technology Consulting group. This group’s primary focus is designing and developing those special utilities/tools to improve the effectiveness of your infrastructure.
Organization Structure #3 (for a large size IT organization)
Question 2: (5 Marks)
Is Just-in-time (JIT) approach helpful in reducing the production cost in any manufacturing organization? Justify your answer with suitable reasons in either case.
Solution:-
JIT has been defined in several ways, including the following:
1. As a production strategy, JIT works to reduce manufacturing costs and to improve quality markedly by waste elimination and more effective use of existing company resources.
2. A philosophy based on the principle of getting the right materials to the right place at the right time.
3. A program that seeks to eliminate nonvalue-added activities from any operation with the objectives of producing this data copied from vu solutions dot com high-quality products (i.e. "zero defects"), high productivity levels, and lower levels of inventory, and developing long term relationships with channel members.
At the heart of the JIT system is the notion that waste should be eliminated. This is in direct contrast to the traditional "just-in-case" philosophy in which large inventories or safely stocks are held just in case they are needed. In JIT, the ideal lot size or EOQ is one unit, safely stock is considered unnecessary, and any inventory should be eliminated.
Many firms have successfully adopted the JIT approach. Companies in industries such as metal products,
automobile manufacturing, electronics, and food and beverage have implemented JIT and realized a number of benefits, including:
1. Productivity improvements and greater control between various production stages.
2. Diminished raw materials, work in process, and finished goods inventory.
3. A reduction in manufacturing cycle times.
4. Dramatically improved inventory turnover rates.
In general, JIT produces benefits for firms in four major areas: improved inventory turns, better customer service, decreased warehouse this data copied from vu solutions dot com space, and improved response time. In addition, reduced distribution costs, lower transportation costs, improved quality of supplier products, and a reduced number of transportation carriers and suppliers can result from the implementation of JIT.
Problems Associated with Implementation JIT
It has some inherent problems which fall into three categories: production scheduling (plant), supplier
production schedules, and supplier locations.
When leveling of the production schedule is necessary due to uneven demand, firms will require higher levels of inventory. Items can be produced during slack periods even though they may not be demanded until a later time, finished goods inventory has a higher value because of its form utility; thus, there is a greater financial risk resulting from product obsolescence, damage, or loss.
However, higher levels of inventory, coupled with a uniform production schedule, can be more advantageous
than a fluctuating schedule with less inventory. In addition, when stockout costs are great because of production slowdowns or shutdowns. JIT may not be the optimal system. JIT reduces inventory levels to the point where there is little if any safety stock, and parts shortages can adversely affect production operations.
Supplier production schedules are a second problem with JIT. Success of a JIT system depends on suppliers' ability to provide parts in accordance with the firm's production schedule. Smaller, more frequent orders can result in higher ordering costs and must be taken into account when calculating any cost savings due to reduced inventory levels. When a large number of small lot quantities are produced, suppliers incur higher production and setup costs. Generally, this data copied from vu solutions dot com suppliers will incur higher costs, unless they are able to achieve the benefits associated with implementing similar systems with their suppliers.
Supplier locations can be a third problem. As distance between the firm and its suppliers increases, delivery times may become more erratic and less predictable. Shipping costs increase as less than truckload (LTL) movements are made. Transit tune variability can cause inventory stockouts that disrupt production scheduling; when this is combined with higher delivery costs on a per unit basis, total costs may be greater than the savings in inventory carrying costs.\
JIT II applies JIT concepts to the purchasing function by having a representative of the supplier locale at the buying organization's facility. Developed by Bose Corporation, this approach improves mutual understanding
between the buyer and supplier, reduces waste and redundancy of efforts, improves supplier responsiveness, and creates a positive working environment.
NOTE: Submit “.doc” file only. Every student should provide his/her own work, exact copying of the assignment (or some portion of the assignment) from this data copied from vu solutions dot com the internet or other students will lead to copy case and zero marks will be awarded. Different softwares will be used to check plagiarism in assignments. Do not put any query on MDB about this assignment, if you have any query then email at cs507@vu.edu.pk
Deadline:
Your assignment must be uploaded/submitted on or before 2nd May 2012.
.......................................
..........................................
Infrastructure, generally, is the set of interconnected structural elements that provide the framework for
supporting the entire structure. It usually applies only to structures that are artificial. The term is used
differently in a variety of fields; perhaps the single most well-known usage is in economics, where it refers
to physical infrastructure such as buildings and roads.
The notion that a structure has an internal framework is popular especially in business organizations where
a dependency on interconnected information technology systems has become as prevalent as a city's
dependency on interconnected conveyance systems for power, people and things. Information
infrastructure consists of the physical facilities services and management that support all computing
resources in an organization. There are five major components of infrastructure
• Computer hardware
• General purpose software
• Networks & communication facilities
• Databases
• Information management personnel
• Each of these components is designed in such manner to collectively meet the needs and objectives
of the organization.
The infrastructure will include
• The detailed configuration of the hardware
• Design of the operating system,
• Documentation of the operational and application software, and
• Documentation on how to technically manage and operate the entire system
• Infrastructure also includes the integration, operation, documentation, maintenance and management
the components as defined in infrastructure.
• It is guideline to how specific computing resources are arranged, operated and managed.
....................
The main benefits of just in time manufacturing system are the following:
Funds that were tied up in inventories can be used elsewhere.
Areas previously used, to store inventories can be used for other more productive uses.
Throughput time is reduced, resulting in greater potential output and quicker response to customers.
Defect rates are reduced, resulting in less waste and greater customer satisfaction.
.................
defining IT Infrastructure :
Information Technology Infrastructure is responsible for the planning, deployment, support, and operation of any organization or industry it targets these areas
maintaining
providing
surrounding mission
software
storing data for later use
.......................................
..........................................
Infrastructure, generally, is the set of interconnected structural elements that provide the framework for
supporting the entire structure. It usually applies only to structures that are artificial. The term is used
differently in a variety of fields; perhaps the single most well-known usage is in economics, where it refers
to physical infrastructure such as buildings and roads.
The notion that a structure has an internal framework is popular especially in business organizations where
a dependency on interconnected information technology systems has become as prevalent as a city's
dependency on interconnected conveyance systems for power, people and things. Information
infrastructure consists of the physical facilities services and management that support all computing
resources in an organization. There are five major components of infrastructure
• Computer hardware
• General purpose software
• Networks & communication facilities
• Databases
• Information management personnel
• Each of these components is designed in such manner to collectively meet the needs and objectives
of the organization.
The infrastructure will include
• The detailed configuration of the hardware
• Design of the operating system,
• Documentation of the operational and application software, and
• Documentation on how to technically manage and operate the entire system
• Infrastructure also includes the integration, operation, documentation, maintenance and management
the components as defined in infrastructure.
• It is guideline to how specific computing resources are arranged, operated and managed.
....................
The main benefits of just in time manufacturing system are the following:
Funds that were tied up in inventories can be used elsewhere.
Areas previously used, to store inventories can be used for other more productive uses.
Throughput time is reduced, resulting in greater potential output and quicker response to customers.
Defect rates are reduced, resulting in less waste and greater customer satisfaction.
.................
defining IT Infrastructure :
Information Technology Infrastructure is responsible for the planning, deployment, support, and operation of any organization or industry it targets these areas
maintaining
providing
surrounding mission
software
storing data for later use









0 comments
Post a Comment